We are delighted to announce the call for scientific abstracts on the One Health Genomics. Celebrating African Excellence in Genomics and Public Health conference. This conference, hosted by the African Centre of Excellence for Genomics of Infectious Diseases (ACEGID), aims to gather researchers, practitioners, and experts from diverse fields to explore the vital role of One Health and Genomics in understanding, preventing, and controlling infectious diseases that affect humans, animals, and the environment. The conference will be held from October 7-9, 2024, at Redeemers University Ede, Nigeria. We invite researchers, scientists, and professionals from academia, industry, and government sectors to submit their abstracts on the following themes:
Abstract Submission
One Health Approach to Disease Surveillance
One Health approach is the holistic study of diseases across human, animal, and environmental health. It emphasizes collaboration and interdependency between various disciplines, including medicine, veterinary science, and environmental science, to address disease transmission at the human-animal-environment interface. By integrating these perspectives, One Health strategies aim to enhance disease surveillance, early detection, and prevention, ultimately mitigating the impact of infectious diseases on both human and animal populations. This session will focus on One Health approaches to disease surveillance with topics and talks highlighting the interdependencies between human, zoonotic, and environmental diseases.

Genomics in Infectious Diseases
Sequencing the genomes of infectious agents helps understand their evolution, drug resistance, and virulence, aiding in developing targeted therapies, vaccines, and diagnostics for infectious diseases. In this session, we will explore animal, human, and environmental genomic topics and capacity-building efforts to expand genomic surveillance and sequencing. This knowledge is crucial for preventing and controlling human and animal health diseases, zoonotic spillover events, and environmental surveillance. Expanding the reach of sequencing in public health, capacity-building efforts focus on training healthcare professionals, researchers, and public health officials to strengthen the capabilities of public health institutions and professionals in genomics and sequencing technologies. By expanding the capacity to perform sequencing, countries can better prepare for outbreaks, improve disease surveillance, and enhance their ability to respond to infectious diseases effectively.

Applications of Pathogen Surveillance
Disease surveillance combines clinical and genomic data to monitor the spread of infectious diseases, track emerging variants, and inform public health interventions. Integrating genomics into surveillance allows for near real-time monitoring of pathogen evolution and transmission patterns, aiding in the rapid response to outbreaks and developing tailored treatments and prevention strategies. This session will focus on human, zoonotic, or environmental surveillance applications.

Advances in Pathogen Detection Tools and Technology
Continuous advancements in diagnostic and detection, genomics, and surveillance tools have led to faster and more accurate methods for identifying pathogens and understanding their genetic makeup. These tools are critical for early detection, tracking, and characterizing infectious agents, leading to more effective disease management. In this session, we will explore novel technologies, tools, and advancements.
Advances in Bioinformatics, Data Visualization, and Data Sharing
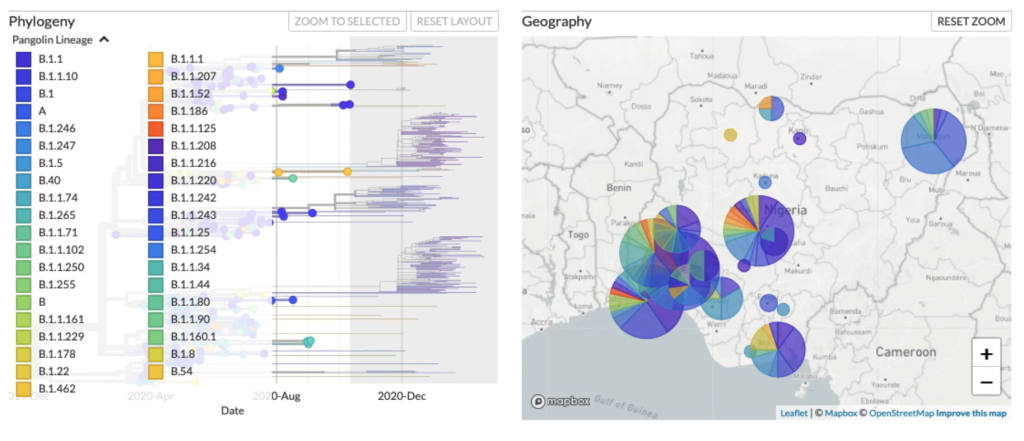
Advances in bioinformatics encompass the development of computational tools and algorithms to analyze and interpret genomic data related to infectious diseases. These tools enable researchers to manage, analyze, and visualize complex genomic datasets effectively. This session will focus on advances in the bioinformatics field, as well as innovations in data visualizations and data sharing. Data visualization and sharing are critical aspects of infectious disease genomics. They involve presenting genomic data in a clear and accessible manner for scientists, healthcare professionals, and the public. Visualizations can help understand genetic data trends and patterns, facilitate collaboration, and inform decision-making in infectious disease management for researchers, clinicians, and the public.
Submission Guidelines:
Abstracts will be accepted in English and must not exceed 300 words. Please provide a clear and concise title for your abstract. Include the names and affiliations of all contributing authors. Indicate the corresponding author and provide their contact details. Abstracts should clearly state the objectives, methods, results, and conclusions of the study. Submissions must be original research, case studies, or review articles. Multiple abstract submissions are allowed.
The abstract submission deadline is July 31st, 2024.
